How Do You Know if It Is a Sigma or Pi Bond
Learning Objectives
- Define sigma and pi bonds.
- Describe hybridization of electrons in sigma and pi bonds.
How many people do you think are squeezed on this street?

Our minds can handle two electrons interacting with one another in a sphere of space. But and so we starting time putting in double bonds and triple bonds. The way we draw these bonds on newspaper suggests we are squeezing more electrons into the same space, and that doesn't work. Electrons don't similar to exist pushed together (particularly since they all accept negative charges that repel 1 some other). Then we need a more circuitous picture that works for all these electrons.
Sigma and Pi Bonds
The hybridization model helps explain molecules with double or triple bonds (see Figure 1 beneath). Ethene (CiiH4) contains a double covalent bond between the 2 carbon atoms and unmarried bonds between the carbon atoms and the hydrogen atoms. The entire molecule is planar.
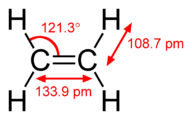
Effigy ane. Geometry of ethene molecule.
Equally tin be seen in the figureabove, the electron domain geometry around each carbon independently is trigonal planar. This corresponds to sp2 hybridization. Previously, we saw carbon undergo sp iii hybridization in a CH 4 molecule, and so the electron promotion is the same for ethene, but the hybridization occurs only betwixt the single s orbital and two of the three p orbitals. Thus generates a fix of three sp 2 hybrids along with an unhybridized 2p z orbital. Each contains 1 electron and so is capable of forming a covalent bond.
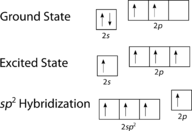
Figure two. Hybridization in ethene.
The three sp 2 hybrid orbitals lie in one aeroplane, while the unhybridized 2pz orbital is oriented perpendicular to that plane. The bonding in C 2 H 4 is explained as follows. One of the three sp 2 hybrids forms a bail past overlapping with the identical hybrid orbital on the other carbon cantlet. The remaining two hybrid orbitals course bonds past overlapping with the 1s orbital of a hydrogen atom. Finally, the 2p z orbitals on each carbon atom form another bail by overlapping with one some other sideways.
Information technology is necessary to distinguish between the two types of covalent bonds in a C2H4 molecule. A sigma bail (![]() bond) is a bail formed by the overlap of orbitals in an end-to-end manner, with the electron density concentrated betwixt the nuclei of the bonding atoms. A pi bond (
bond) is a bail formed by the overlap of orbitals in an end-to-end manner, with the electron density concentrated betwixt the nuclei of the bonding atoms. A pi bond (![]() bond) is a bond formed by the overlap of orbitals in a side-past-side fashion with the electron density concentrated above and beneath the plane of the nuclei of the bonding atoms. The effigybelow shows the ii types of bonding in C2Hfour. The sp2 hybrid orbitals are regal and the p z orbital is blue. Three sigma bonds are formed from each carbon atom for a full of six sigma bonds full in the molecule. The pi bond is the "2nd" bail of the double bonds between the carbon atoms and is shown as an elongated green lobe that extends both above and below the plane of the molecule. This plane contains the vi atoms and all of the sigma bonds.
bond) is a bond formed by the overlap of orbitals in a side-past-side fashion with the electron density concentrated above and beneath the plane of the nuclei of the bonding atoms. The effigybelow shows the ii types of bonding in C2Hfour. The sp2 hybrid orbitals are regal and the p z orbital is blue. Three sigma bonds are formed from each carbon atom for a full of six sigma bonds full in the molecule. The pi bond is the "2nd" bail of the double bonds between the carbon atoms and is shown as an elongated green lobe that extends both above and below the plane of the molecule. This plane contains the vi atoms and all of the sigma bonds.

Figure iii. Sigma and pi bonds.
In a conventional Lewis electron-dot structure, a double bond is shown as a double nuance betwixt the atoms as in C=C. It is important to realize, still, that the two bonds are unlike: one is a sigma bond, while the other is a pi bond.
Ethyne (C 2 H two ) is a linear molecule with a triple bond betwixt the two carbon atoms (see Effigy 4). The hybridization is therefore sp .
![]()
Figure four. Ethyne structure.
The promotion of an electron in the carbon atom occurs in the same way. However, the hybridization now involves but the 2s orbital and the 2p ten orbital, leaving the 2p y and the 2p z orbitals unhybridized.
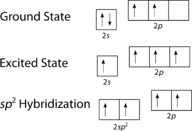
Figure 5. Hybridization in ethyne.
The sp hybrid orbitals form a sigma bail between each other as well equally sigma bonds to the hydrogen atoms. Both the p y and the p z orbitals on each carbon atom form pi bonds between each other. As with ethene, these side-to-side overlaps are above and below the aeroplane of the molecule. The orientation of the two pi bonds is that they are perpendicular to i another (encounterFigure vi below). 1 pi bond is above and below the line of the molecule equally shown, while the other is in front of and behind the folio.

Effigy 6. The CiiH2 molecule contains a triple bail betwixt the two carbon atoms, ane of which is a sigma bond, and two of which are pi bonds.
In general, single bonds between atoms are e'er sigma bonds. Double bonds are comprised of 1 sigma and 1 pi bond. Triple bonds are comprised of one sigma bond and ii pi bonds.
Summary
- Sigma bonds grade between two atoms.
- Pi bonds course from p orbital overlap.
Practice
Utilize the link below to answer the following questions:
https://sites.google.com/site/ed350201003/Job
- What kind of overlap makes a sigma bond?
- What kind of overlap makes a pi bail?
- Tin a sigma bail be formed by overlapping an s and a p orbital?
- In marsh gas, which carbon electrons are not involved in bonding?
Review
- What is the hybridization around each carbon in ethene?
- What are the ii bonds in C=C?
- What is the shape of the ethene molecule?
- How are the ethyne pi bonds oriented in relation to each other?
Glossary
Source: https://courses.lumenlearning.com/cheminter/chapter/sigma-and-pi-bonds/
0 Response to "How Do You Know if It Is a Sigma or Pi Bond"
Post a Comment